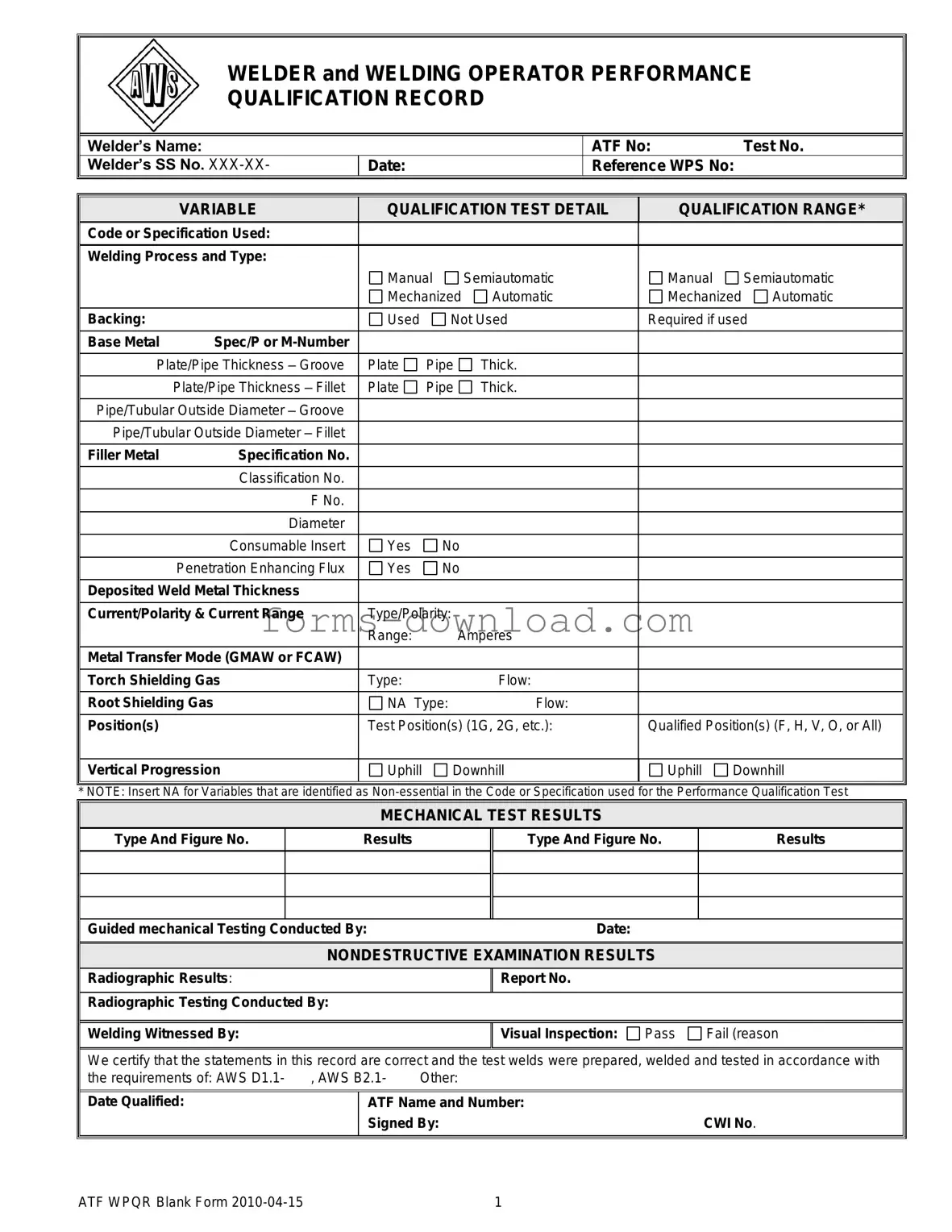
Blank Welder Performance Qualification Record Form
The Welder Performance Qualification Record form serves as a crucial document in the welding industry, capturing essential details about a welder's qualifications and competencies. It includes the welder's name, identification numbers, and the date of the qualification test, ensuring that each record is unique and traceable. The form outlines the specific welding processes utilized, such as manual or automatic methods, and specifies the type of base metals and filler materials involved. It also provides information on the thickness of the materials being welded, as well as the diameter of pipes or tubular structures, which are key factors in determining a welder's skill level. Furthermore, the form details the test positions and progression, indicating whether the welding was performed in an uphill or downhill manner. Important results from mechanical tests and non-destructive examinations, such as radiographic testing, are also documented, affirming the integrity of the welds produced. By certifying that all statements within the record are accurate, the form not only validates a welder’s capabilities but also ensures compliance with industry standards, such as those set forth by the American Welding Society. This comprehensive documentation plays a vital role in maintaining safety and quality in welding practices across various sectors.
More PDF Forms
Form D1 ‘Application for a Driving Licence’ - Answer if your name or address has changed since your last licence was issued.
To facilitate the transfer process, obtaining a Bill Of Sale for a Motorcycle is a key step, as it helps avoid any potential disputes regarding the ownership of the motorcycle, providing both parties with a clear record of the transaction.
Light Bill Template - Useful in preparing for service changes or relocations associated with utilities.
Dekalb County Water Application Online - Understanding the terms of service is important before committing to a water account.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Welder Performance Qualification Record form, there are several important dos and don’ts to keep in mind. Following these guidelines will help ensure the form is completed accurately and efficiently.
- Do provide accurate personal information, including the welder’s name and ATF number.
- Do ensure that all test details are filled out completely, including the reference WPS number.
- Do indicate the welding process and type clearly, specifying whether it’s manual, semiautomatic, or automatic.
- Do verify the mechanical test results and ensure they are documented correctly.
- Don’t leave any required fields blank; missing information can lead to delays in processing.
- Don’t forget to include the signatures of all relevant parties involved in the testing and qualification process.
Welder Performance Qualification Record Sample

WELDER and WELDING OPERATOR PERFORMANCE
QUALIFICATION RECORD
|
Welder’s Name: |
|
|
|
|
ATF No: |
|
Test No. |
||||||
|
Welder’s SS No. |
|
Date: |
|
|
Reference WPS No: |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
VARIABLE |
|
|
QUALIFICATION TEST DETAIL |
|
|
QUALIFICATION RANGE* |
|
|||||
|
Code or Specification Used: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Welding Process and Type: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Manual |
Semiautomatic |
|
|
Manual |
|
Semiautomatic |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Mechanized |
Automatic |
|
|
Mechanized |
Automatic |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Backing: |
|
|
|
Used |
Not Used |
|
|
Required if used |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Base Metal |
Spec/P or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Plate/Pipe Thickness – Groove |
|
Plate |
Pipe |
Thick. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Plate/Pipe Thickness – Fillet |
|
Plate |
Pipe |
Thick. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Pipe/Tubular Outside Diameter – Groove |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Pipe/Tubular Outside Diameter – Fillet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filler Metal |
Specification No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Classification No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diameter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consumable Insert |
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Penetration Enhancing Flux |
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Deposited Weld Metal Thickness |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Current/Polarity & Current Range |
|
Type/Polarity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Range: |
Amperes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Metal Transfer Mode (GMAW or FCAW) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Torch Shielding Gas |
|
Type: |
|
Flow: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Root Shielding Gas |
|
NA Type: |
Flow: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Position(s) |
|
|
|
Test Position(s) (1G, 2G, etc.): |
|
|
Qualified Position(s) (F, H, V, O, or All) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Vertical Progression |
|
Uphill |
Downhill |
|
|
Uphill |
Downhill |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* NOTE: Insert NA for Variables that are identified as
|
|
|
|
MECHANICAL TEST RESULTS |
|
|
||
|
Type And Figure No. |
|
|
Results |
|
Type And Figure No. |
Results |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Guided mechanical Testing Conducted By: |
|
Date: |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NONDESTRUCTIVE EXAMINATION RESULTS |
|
|
|||
|
Radiographic Results: |
|
|
|
Report No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Radiographic Testing Conducted By: |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Welding Witnessed By: |
|
|
|
Visual Inspection: Pass |
Fail (reason |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
We certify that the statements in this record are correct and the test welds were prepared, welded and tested in accordance with |
|||||||
|
the requirements of: AWS D1.1- |
, AWS B2.1- |
Other: |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Date Qualified: |
|
ATF Name and Number: |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Signed By: |
CWI No. |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
ATF WPQR Blank Form |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|||
Listed Questions and Answers
-
What is the purpose of the Welder Performance Qualification Record (WPQR)?
The WPQR serves as a formal documentation of a welder's qualifications and abilities. It verifies that the welder has successfully completed a series of tests according to specific codes and standards, demonstrating proficiency in various welding processes and techniques.
-
What information is included in the WPQR?
The WPQR contains essential details such as the welder's name, identification numbers, test numbers, and the date of qualification. It also specifies the welding processes used, the base metal specifications, filler metal classifications, and the test positions. Additionally, it includes results from mechanical tests and non-destructive examinations.
-
What types of welding processes are covered by the WPQR?
The WPQR encompasses various welding processes, including manual, semiautomatic, mechanized, and automatic welding. Each process type is specified to ensure that the welder's qualifications align with the requirements of the job.
-
How is the qualification range determined?
The qualification range is determined by the variables specified in the applicable code or specification. Factors such as base metal thickness, filler metal specifications, and the positions in which the welder is qualified all contribute to defining this range.
-
What are the mechanical test results, and why are they important?
Mechanical test results provide data on the strength and durability of the welds produced by the welder. These results are crucial because they help assess whether the welder meets the required standards for the specific welding application, ensuring safety and reliability in the final product.
-
What role does non-destructive examination play in the qualification process?
Non-destructive examination (NDE) is a critical part of the qualification process as it evaluates the integrity of the welds without causing damage. Techniques such as radiographic testing are employed to identify any defects or inconsistencies, ensuring that the welds meet the necessary quality standards.
-
Who is responsible for conducting the tests and examinations?
Tests and examinations are typically conducted by certified individuals or organizations. The WPQR should indicate the names and credentials of those conducting the mechanical tests and non-destructive examinations to ensure accountability and credibility.
-
How long is a WPQR valid?
The validity of a WPQR can vary depending on the specific codes and standards governing the welding process. Generally, a WPQR remains valid as long as the welder continues to practice their skills and the conditions under which they were qualified do not change significantly.
-
What happens if a welder fails a qualification test?
If a welder fails a qualification test, they must review the areas of deficiency and receive additional training or practice before retesting. The qualification process is designed to ensure that only competent welders are certified, thus maintaining high standards in the industry.
Form Overview
| Fact Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Welder Performance Qualification Record form verifies a welder's ability to perform welding tasks according to specified standards. |
| Key Information | It includes essential details such as the welder's name, identification numbers, and test specifics. |
| Welding Processes | The form accommodates various welding processes, including manual, semiautomatic, mechanized, and automatic methods. |
| Test Positions | It specifies test positions (e.g., 1G, 2G) and qualified positions (e.g., F, H, V) for comprehensive qualification. |
| Mechanical Testing | Results from guided mechanical testing must be documented, ensuring compliance with industry standards. |
| Non-Destructive Examination | Radiographic results and visual inspection outcomes are included to confirm the quality of welds. |
| Governing Standards | This form is typically governed by standards such as AWS D1.1 and AWS B2.1, depending on the state and application. |